LLM token streaming with htmx
LLM-based chat interfaces like ChatGPT use token streaming to incrementally display generated text, rather than having users wait for the full response. This technique improves the user experience by reducing perceived latency, especially for lengthy outputs.1
Token streaming can be easily implemented in server-driven web applications using htmx, a library that enables dynamic interfaces using HTML attributes and server-sent events (SSE). This article demonstrates an example using Python and Flask, though htmx is backend-agnostic and can be used with any tech stack.
Project setup
We’ll incorporate token streaming into a simple chat app. Start by following the Flask documentation to set up a new project. Then, create routes for a static page and form handler:
# app.py
from flask import Flask, request
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route("/")
def index():
return app.send_static_file("index.html")
@app.post("/chat")
def chat():
query = request.form["query"]
return f"<article>{query}</article>"<!-- static/index.html -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<meta name="color-scheme" content="light dark" />
<!-- Load htmx and SSE extension -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/htmx.org@2.0.4"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/htmx-ext-sse@2.2.2"></script>
<!-- Pico CSS for predefined styles -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@picocss/pico@2/css/pico.classless.min.css" />
</head>
<body>
<main>
<!-- Form for sending queries to the `/chat` endpoint -->
<form hx-post="/chat" hx-target="#answer">
<fieldset role="group">
<input name="query" placeholder="Ask me anything" />
<input type="submit" value="Send" />
</fieldset>
</form>
<!-- Container for receiving `/chat` response -->
<div id="answer"></div>
</main>
</body>
</html>
The <form> sends queries to the /chat endpoint using hx-post, and the server responds with an HTML fragment that is swapped into the #answer target element.
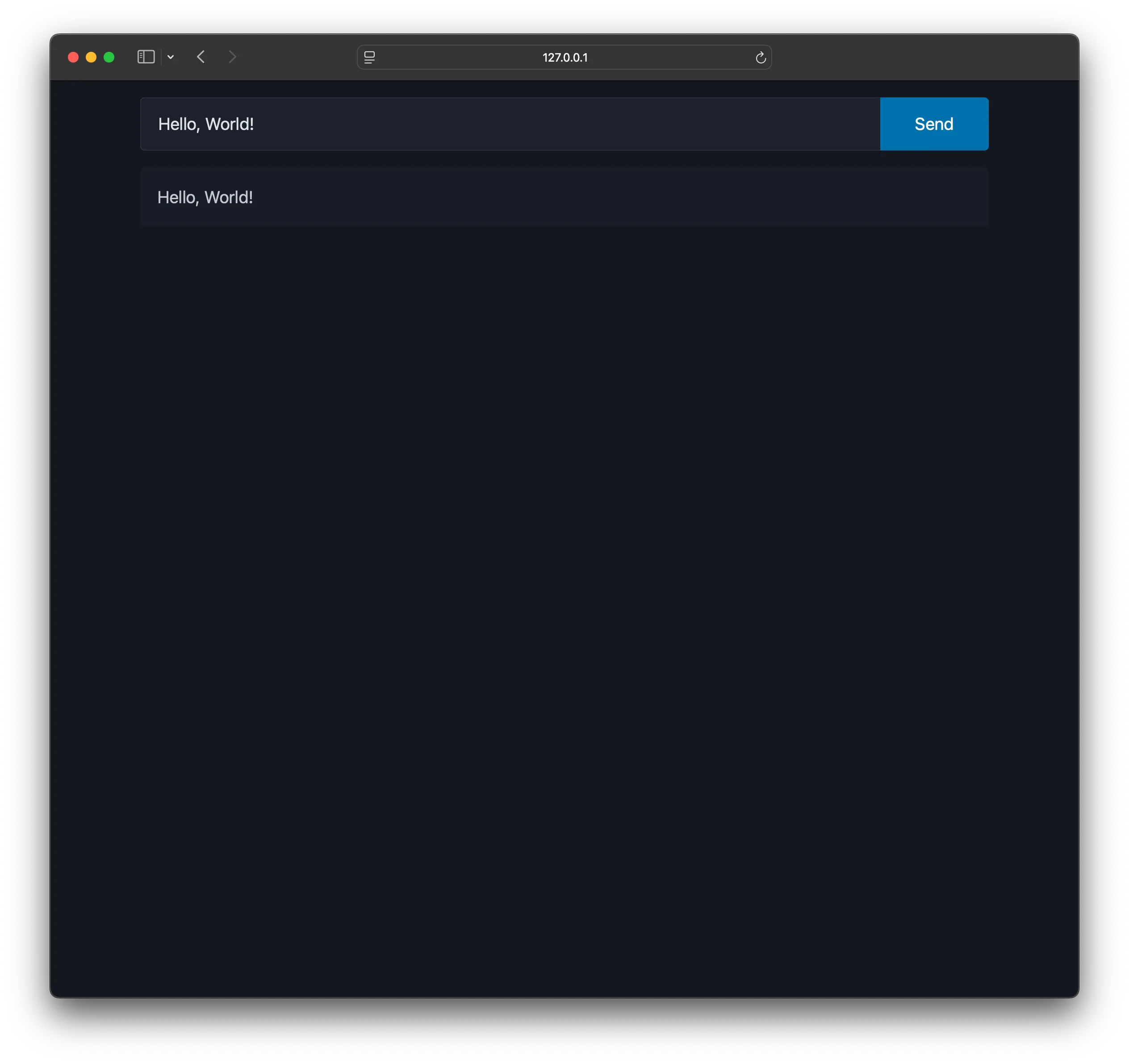
Start the server using flask run and visit the site at the logged URL (e.g., http://127.0.0.1:5000). After submitting a query, the same text should appear on the page.
Plain text streaming
To implement basic text streaming, start by updating the /chat handler:
@app.post("/chat")
def chat():
query = request.form["query"]
return f"""
<article hx-ext="sse"
sse-connect="/stream?query={query}"
sse-swap="token"
hx-swap="beforeend scroll:bottom"
sse-close="close"></article>
"""The new fragment contains various attributes to initialize the token stream:
hx-extenables the htmx SSE extension.sse-connectspecifies the streaming endpoint.sse-swapspecifies the events to swap into the DOM.hx-swapappends each token into the current element and scrolls to the bottom.sse-closespecifies the event that closes the stream.
We’ll use Ollama to generate responses from a local LLM. Refer to the Ollama documentation to get started with your preferred model. Then, install the Ollama Python library and set up the /stream route:
from flask import Flask, Response, request, stream_with_context
import ollama
# -- omitted -- #
prompt = "Answer the query in plain text"
model = "phi4"
@app.route("/stream")
def stream():
def generate():
stream = ollama.chat(
model=model,
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": request.args["query"]},
],
stream=True,
)
for chunk in stream:
token = chunk["message"]["content"].replace("\n", "<br>")
yield server_sent_event("token", token)
yield server_sent_event("close", "")
return Response(stream_with_context(generate()), mimetype="text/event-stream")
def server_sent_event(event: str, data: str) -> str:
return f"event: {event}\ndata: {data}\n\n"
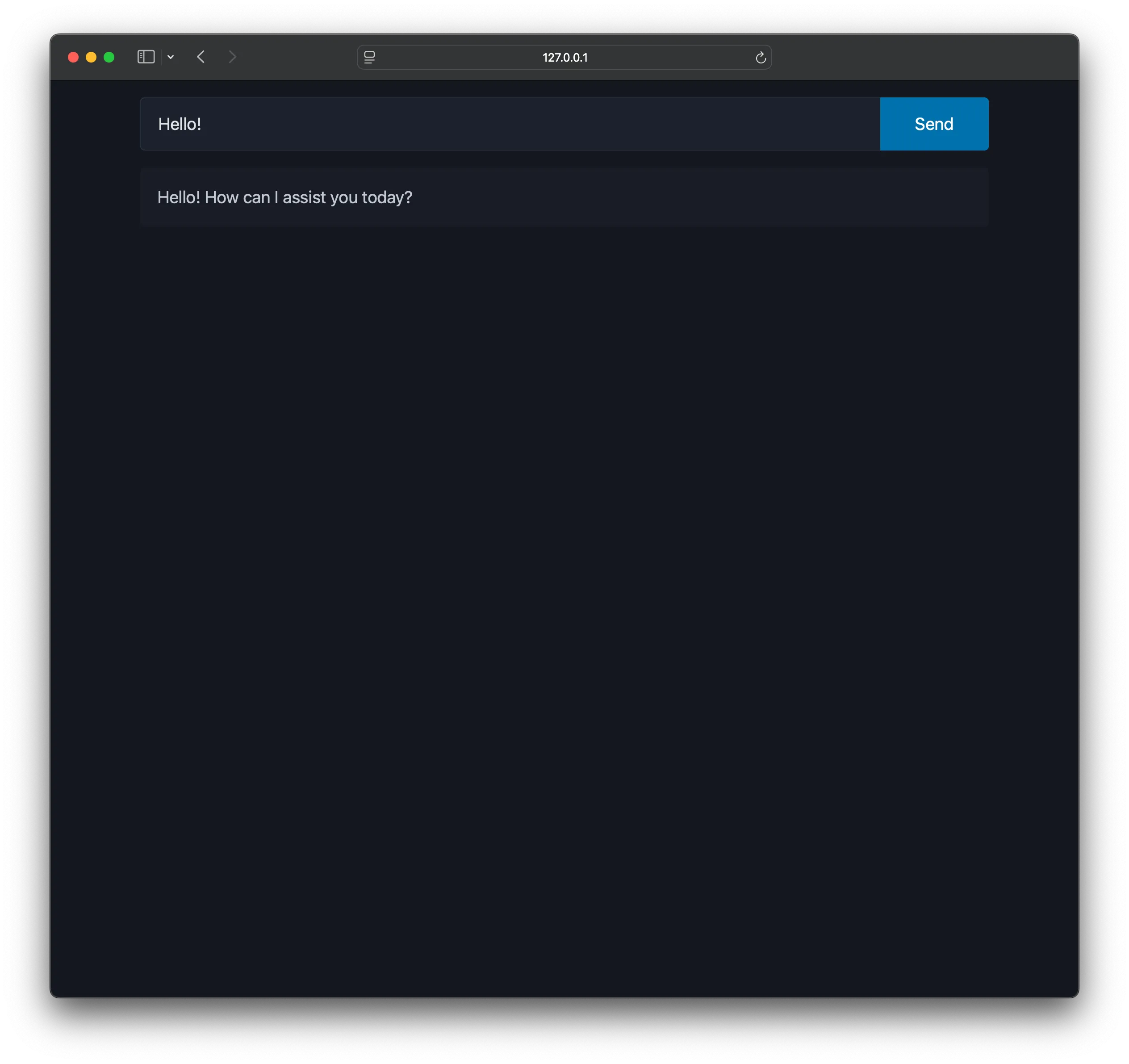
The handler streams generated tokens to the client, wrapping each one with server_sent_event() according to the SSE specification2. Server-sent events must end with \n\n, so newlines outputted by the model are replaced with <br> to prevent message truncation. Once all tokens are sent, a close message ends the stream.
HTML streaming
To generate HTML instead of plain text, we can modify the prompt:
prompt = "Answer the query in only HTML in a <div> fragment (never use full <html> or backticks)"However, the output will unfortunately appear malformed.
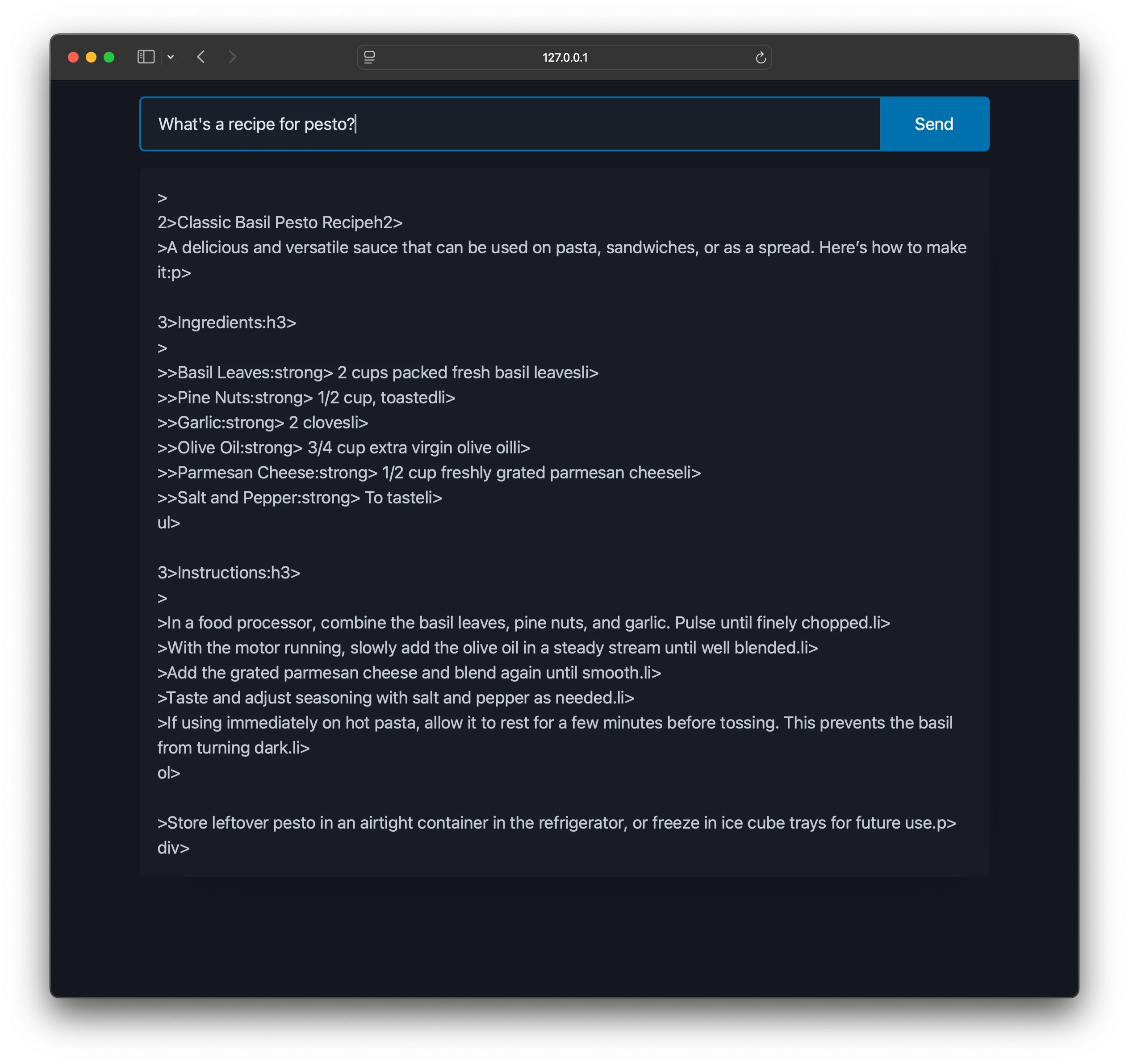
The incomplete HTML tags aren’t being correctly interpreted, even after subsequent tokens complete the element. A simple solution involves buffering the HTML client-side and re-rendering from the buffer, rather than appending directly to the DOM.
The updated server code disables hx-swap and adds improved newline handling for HTML:
@app.post("/chat")
def chat():
query = request.form["query"]
# Disable htmx swapping with "hx-swap=none"
return f"""
<article hx-ext="sse"
sse-connect="/stream?query={query}"
sse-swap="token"
hx-swap="none"
sse-close="close"></article>
"""
@app.route("/stream")
def stream():
def generate():
# -- omitted -- #
buffer = ""
in_pre = False
for chunk in stream:
for token in chunk["message"]["content"]:
# Add newlines only for <pre> blocks
if token == "\n":
if in_pre:
token = "<br/>"
else:
buffer += token
if buffer.endswith("<pre>"):
in_pre = True
if buffer.endswith("</pre>"):
in_pre = False
yield server_sent_event("token", token)
yield server_sent_event("close", "")
Add JavaScript listeners to hook into htmx events for updating the buffer and target element:
<script>
window.answer = ""; // Buffer for accumulating SSE data
// Append tokens to buffer and re-render target element
document.addEventListener("htmx:sseBeforeMessage", event => {
answer += event.detail.data;
event.detail.elt.innerHTML = answer;
});
// Reset the buffer after completion
document.addEventListener("htmx:sseClose", () => (answer = ""));
</script>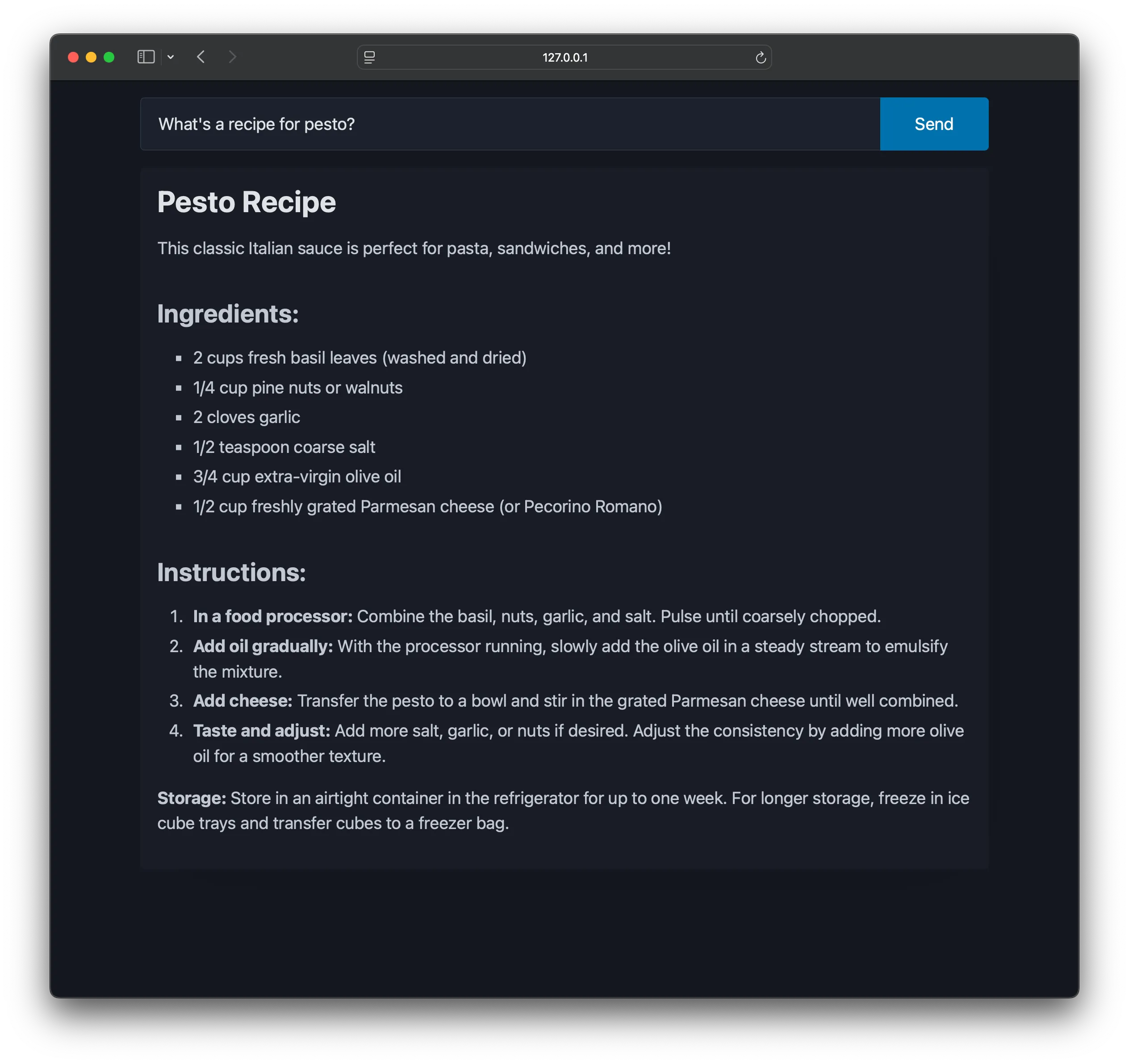
The final code is available on GitHub. Further enhancements could include updating the DOM only when the buffer contains complete HTML tags to prevent flickering or using CSS transitions for smoother rendering.